Image Type
Posterior Atlantodental Interval (PADI)
1) Description of Measurement
PADI represents the functional spinal canal diameter at the C1–C2 level. It directly estimates the space available for the spinal cord and is a strong predictor of neurologic risk.
2) Instructions to Measure
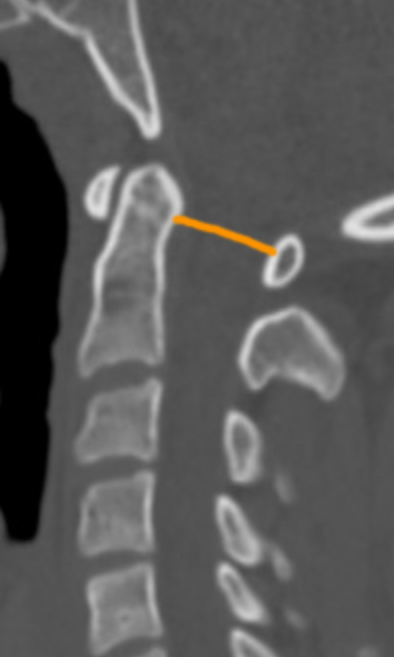
On sagittal CT, identify:
The posterior surface of the dens
The anterior surface of the posterior arch of C1
Measure the minimal distance between these two points.
PADI should be assessed in flexion, as this position typically maximizes C1 anterior translation and reduces the canal diameter, representing the "worst-case scenario" for the spinal cord.
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Normal: >14 mm
Values ≤14 mm are associated with increased risk of myelopathy, particularly in rheumatoid arthritis or traumatic instability.
A PADI of less than 10 mm represents absolute canal stenosis, where the cord is likely compressed even in the neutral position
4) Important References
Bono CM, Vaccaro AR, Fehlings M, et al. Measurement techniques for upper cervical spine injuries: consensus statement of the spine trauma study group. Spine. 2007;32:593-600.
Joaquim, A. F., Ghizoni, E., Tedeschi, H., Appenzeller, S., & Riew, K. D. (2015). Radiological evaluation of cervical spine involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Neurosurgical focus, 38(4), E4. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.1.FOCUS14664
Rojas C, Bertozzi J, Martinez C, Whitlow J. Reassessment of the Craniocervical Junction: Normal Values on CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(9):1819-23. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0660 - Pubmed
Boden SD, Dodge LD, Bohlman HH, Rechtine GR. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine. A long-term analysis with predictors of paralysis and recovery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75:1282–1297. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199309000-00004.
Adapted from: Knipe H, Atlantodental interval. Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 17 Dec 2025). https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-38418