Image Type
Atlantodental Interval (ADI)
1) Description of Measurement
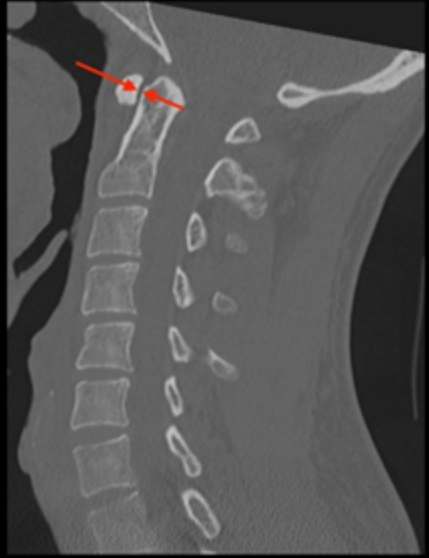
The distance between the anterior arch of C1 (atlas) and the odontoid process (dens) of C2. It reflects the integrity of the transverse atlantal ligament, which restrains anterior translation of C1 on C2.
2) Instructions to Measure
Use a midsagittal CT reconstruction.
Identify the posterior cortex of the anterior arch of C1 and the anterior cortex of the dens.
Measure the shortest distance between these two structures at the midportion of the dens.
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Adults: <3 mm
Pediatric population: <5 mm
Increased values indicate atlantoaxial instability, commonly due to trauma, inflammatory disease, or congenital ligamentous laxity.
Pathologic widening of the ADI occurs when the transverse ligament is disrupted (trauma), attenuated (Down syndrome, Morquio syndrome), or eroded (Rheumatoid Arthritis).
4) Important References
Bono CM, Vaccaro AR, Fehlings M, et al. Measurement techniques for upper cervical spine injuries: consensus statement of the spine trauma study group. Spine. 2007;32:593-600.
Bucholz RW, Burkhead WZ. The pathological anatomy of fatal atlanto-occipital dislocations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:248-250.
Rojas C, Bertozzi J, Martinez C, Whitlow J. Reassessment of the Craniocervical Junction: Normal Values on CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(9):1819-23. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0660 - Pubmed
Bertozzi J, Rojas C, Martinez C. Evaluation of the Pediatric Craniocervical Junction on MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(1):26-31. doi:10.2214/ajr.08.1058 - Pubmed
5) Other info....
Although closely related, they serve distinct clinical purposes: the ADI is a diagnostic measure of ligamentous competence, whereas the PADI is a prognostic measure of neurological risk.
Adapted from: Knipe H, Atlantodental interval. Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 17 Dec 2025). https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-38418