Image Type
C2 Tilt
1) Description of Measurement
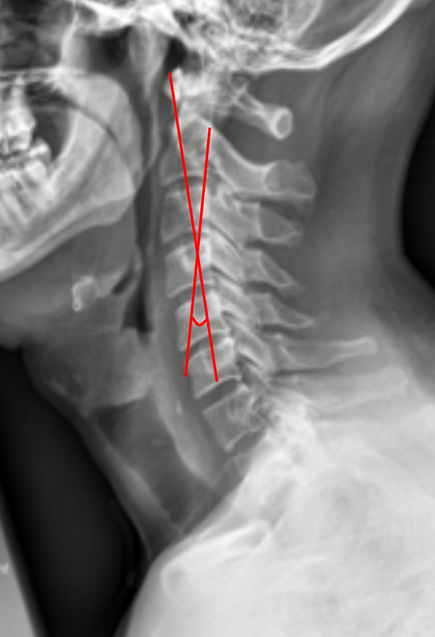
C2 Tilt quantifies the inclination of the axis (C2 vertebra) relative to the vertical axis of the cervical spine and a line drawn parallel to the posterior cortex of the odontoid and is an important parameter for assessing cervical sagittal alignment.
It provides insight into the orientation of the upper cervical spine, often used in conjunction with C2–C7 lordosis and cSVA (C2–C7 sagittal vertical axis) to evaluate cervical balance, especially in deformity correction or postoperative analysis.
A forward-tilting C2 body may reflect compensatory alignment in response to subaxial deformity or global sagittal imbalance.
2) Instructions to Measure
Obtain a neutral, standing lateral cervical spine X-ray
Identify the inferior endplate of C2
Draw a horizontal line along the inferior endplate of C2
Draw a true vertical reference line perpendicular to the inferior endplate
Draw a line parallel to the posterior cortex of the odontoid
Measure the angle between the reference line and the posterior odontoid line
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Normal C2 Tilt: 15-25° anterior inclination; reflects normal upper cervical alignment
C2 Tilt > 25°: may indicate anterior head translation and/or positive sagittal imbalance
C2 Tilt < 15°: may be associated with hypolordosis or compensatory posterior tilt
4) Important References
Divi SN, Bronson WH, Canseco JA, et al. How do C2 tilt and C2 slope correlate with patient reported outcomes in patients after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion? The Spine Journal. 2021. 21(4): 578-585.
Tang JA, Scheer JK, Smith JS, et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Neurosurgery. 2012;71(3):662–669.
Iyer S, Lenke LG, Nemani VM, et al. Impact of cervical sagittal alignment parameters on patient-reported outcomes after posterior cervical fusion. Spine. 2016;41(23):1790–1798.
Kato M, Namikawa T, Matsumura A, et al. C2–C7 sagittal vertical axis and cervical tilt: relationships with cervical alignment and clinical outcomes. Spine. 2016;41(3):E160–E168.
Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Ames CP, et al. Assessment of cervical sagittal alignment and clinical implications. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(2):141–159.
5) Other info....
C2 tilt correlates with global cervical sagittal imbalance - higher values (more forward tilt) are linked to increased cSVA and higher Neck Disability Index (NDI) scores.
It directly influences chin-brow vertical angle (CBVA) and horizontal gaze maintenance.
In surgical planning, restoring physiological C2 tilt can help optimize global sagittal alignment and reduce postoperative compensatory mechanisms.
Consider evaluating C2 slope, T1 slope, and C2–C7 SVA together for comprehensive sagittal analysis.