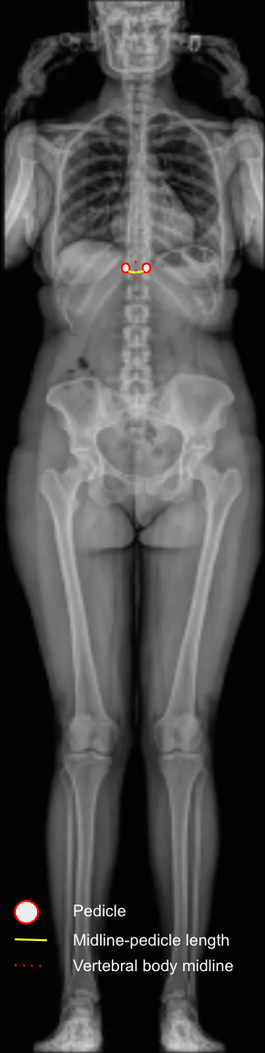
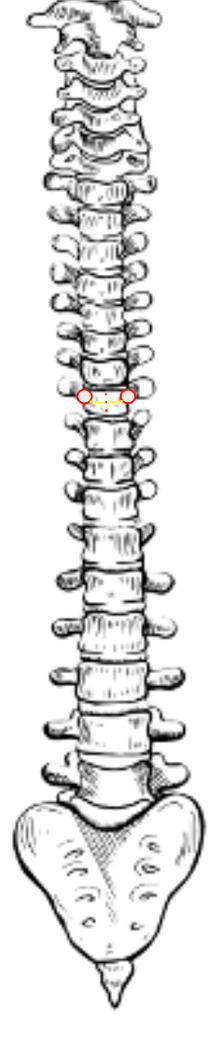
Image Type
Apical Vertebral Rotation (AVR) - Nash-Moe classification
1) Description of Measurement
The Apical Vertebral Rotation (AVR) quantifies the degree of vertebral rotation around the longitudinal axis of the spine, most often assessed in patients with scoliosis on a standing PA or AP full-spine X-ray.
AVR provides information on the axial component of the scoliotic deformity, complementing the coronal (Cobb angle) and sagittal (kyphosis/lordosis) measurements.
It reflects rib hump prominence and trunk asymmetry, influencing both the cosmetic and biomechanical impact of scoliosis.
AVR measurement is key for monitoring curve progression, brace effectiveness, and surgical correction (particularly derotation maneuvers).
2) Instructions to Measure
Obtain a standing PA or AP full-length spine X-ray with the entire spine, pelvis, and ribs included.
Identify the apical vertebra of the scoliotic curve — the most laterally displaced and rotated vertebra at the curve apex.
Nash–Moe Method (most widely used):
Locate the pedicles of the apical vertebra.
Assess the asymmetry of pedicle shadows: in a normal spine, pedicles are symmetric and equidistant from the vertebral margins.
As rotation increases, the pedicle on the convex side moves toward the midline, while the pedicle on the concave side may disappear.
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Grade 0: ~ 0° rotation; both pedicles equidistant from vertebral margins
Grade 1: ~25° rotation; convex-side pedicle moves slightly toward midline
Grade 2: ~50° rotation; convex-side pedicle at midline
Grade 3: ~75° rotation; convex-side pedicle crosses midline
Grade 4: ~100° rotation; convex-side pedicle beyond midline; concave pedicle not visible
4) Important References
Nash CL Jr, Moe JH. A study of vertebral rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(2):223–229.
Perdriolle R, Vidal J. Thoracic idiopathic scoliosis curve evolution and prognosis. Spine. 1985;10(9):785–791.
Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(8):1169–1181.
Stokes IAF, Aronsson DD. Measurement of vertebral rotation in idiopathic scoliosis using digital radiographs. Spine. 2001;26(16):1809–1815.
Kuklo TR, Lenke LG, Graham EJ, et al. Correlation of radiographic, clinical, and cosmetic deformity in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2002;27(18):E387–E393.
5) Other info....
AVR reflects axial deformity, which cannot be assessed from Cobb angle alone.
It is a critical determinant of rib hump prominence and cosmetic asymmetry.
Modern 3D imaging (EOS, CT, or surface topography) can provide more accurate rotational analysis, but X-ray–based AVR remains the standard clinical method.
Rotation is typically toward the convex side of the curve.
In postoperative evaluation, reduced AVR indicates successful derotation correction.
For research or detailed assessment, 3D reconstruction or biplanar low-dose EOS imaging can quantify AVR in true degrees.
When following scoliosis progression, consistency in measurement technique and observer is critical for reliable comparison.