Image Type
Pars Interarticularis Defects
1) Description of Measurement
Assessment of the pars interarticularis evaluates for spondylolysis, stress reactions, or chronic non-union, which are common in young athletes, degenerative spondylolisthesis, and in association with lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (Bertolotti’s syndrome). Key features include:
Defect width
Cortical continuity
Marginal sclerosis
These features distinguish acute stress fractures from chronic pars defects.
2) Instructions to Measure
Scroll to the true parasagittal slice through the pars at the affected level.
Identify the pars region between the superior and inferior articular processes.
Assess Continuity:
Intact cortex → normal
Lucent cleft → pars defect
Measure Defect Width (mm):
At the widest part of the lucent gap, measure from one cortical margin to the other.
Evaluate Sclerosis:
Note increased cortical density along the defect margins (chronic stress reaction).
Repeat bilaterally and at adjacent levels.
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Cortical continuity
Normal: Intact
Acute Stress Reaction: Partial disruption
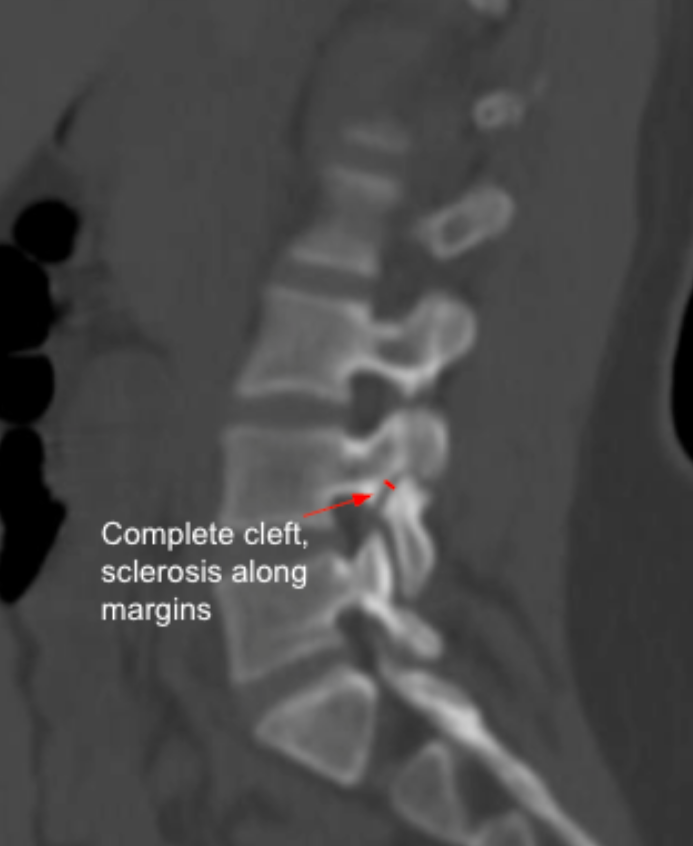
Chronic Pars Defect: Complete cleft
Defect Width
Normal: 0 mm
Acute Stress Reaction: < 2 mm
Chronic Pars Defect: ≥ 2-3 mm
Sclerosis
Normal: None
Acute Stress Reaction: Minimal
Chronic Pars Defect: Prominent marginal sclerosis
Alignment
Normal: No slip
Acute Stress Reaction: No or minimal slip
Chronic Pars Defect: Associated with spondylolisthesis
4) Important References
Hammerberg KW. New concepts on the pathogenesis and classification of spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005 Mar 15;30(6 Suppl):S4-11. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000155576.62159.1c.
Campbell RS, Grainger AJ, Hide IG, et al. Juvenile spondylolysis: a comparative analysis of CT, SPECT and MRI. Skeletal Radiol. 2005 Feb;34(2):63-73. doi: 10.1007/s00256-004-0878-3. Epub 2004 Nov 25.
Pereira Duarte M, Camino Willhuber GO. Pars Interarticularis Injury. 2023 Feb 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–.
Rakauskas TR, Gallup S, Mohamed AA, et al. An update on the prevalence and management of Bertolotti's syndrome. Front Surg. 2024 Dec 12;11:1486811. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1486811.
5) Other info....
Defect width > 3 mm with sclerosis strongly indicates chronic non-union.
Early stress reactions may be CT-negative; MRI STIR is more sensitive for marrow edema.
Bilateral pars defects commonly precede isthmic spondylolisthesis.
Adapted from: Radswiki T, Gaillard F, Hacking C, et al. Spondylolysis. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 04 Jan 2026) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-12262