Image Type
Disc Herniation Size
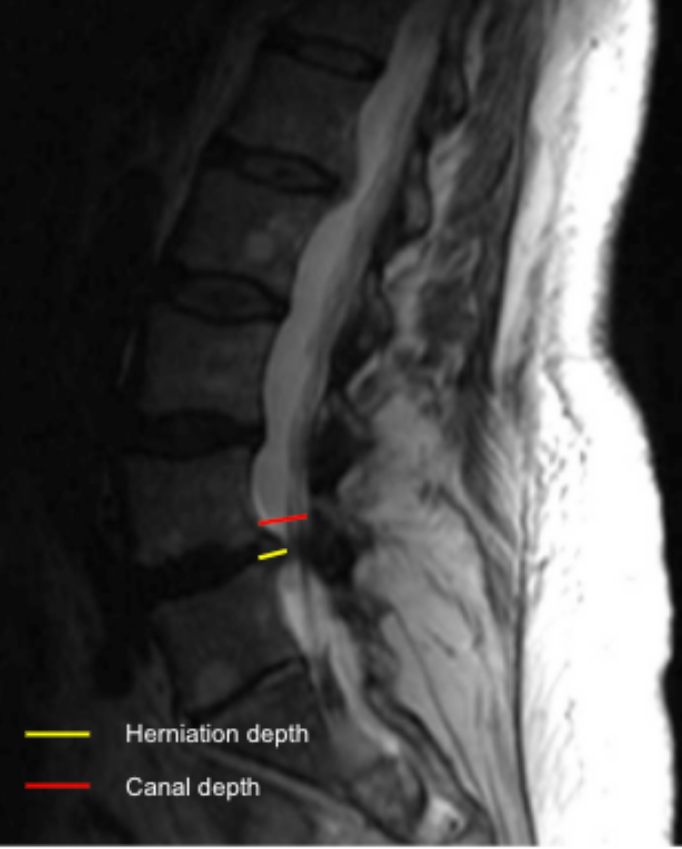
1) Description of Measurement
Disc herniation size quantifies the degree of posterior disc displacement beyond the normal vertebral body margin and expresses the extent of neural element encroachment. It can be reported as:
Absolute protrusion depth (mm), or
Relative size (%), calculated as a ratio of herniation depth to the anteroposterior diameter of the spinal canal at the same level.
This measurement is essential for grading severity, surgical planning, and correlating imaging with radicular symptoms.
2) Instructions to Measure
Identify the disc level with the maximum posterior disc protrusion.
On the mid-sagittal or parasagittal slice:
Draw a reference line along the posterior margin of the adjacent vertebral bodies (baseline).
Measure the maximum herniation depth (HD):
Draw a perpendicular line from the baseline to the most posterior point of the herniated disc material (mm).
Measure the AP spinal canal diameter (CD) at the same level.
Calculate relative herniation size (%):
Relative Size = HD/CD*100
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Mild herniation: < 3 mm or < 20% canal
Moderate herniation: 3 - 5 mm or 20-40% canal
Severe herniation: > 5 mm or > 40 % canal
Key points:
Herniations occupying > 40% of canal diameter are strongly associated with symptomatic nerve root compression.
4) Important References
Fardon DF, Williams AL, Dohring EJ, et al. Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology. Spine J. 2014 Nov 1;14(11):2525-45. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.04.022.
Modic MT, Ross JS. Lumbar degenerative disk disease. Radiology. 2007 Oct;245(1):43-61. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2451051706.
Jensen MC, Kelly AP, Brant-Zawadzki MN. MRI of degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Magn Reson Q. 1994 Sep;10(3):173-90.
5) Other info....
Always specify:
Location (central, paracentral, foraminal, extraforaminal)
Type (bulge, protrusion, extrusion, sequestration)
Correlate with:
Dural sac CSA
Lateral recess width
Foraminal dimensions
Adapted from: Feger J, Er A, Yap J, et al. Lumbar spine protocol (MRI). Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 01 Jan 2026) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-147093