Image Type
Dural Sac CSA
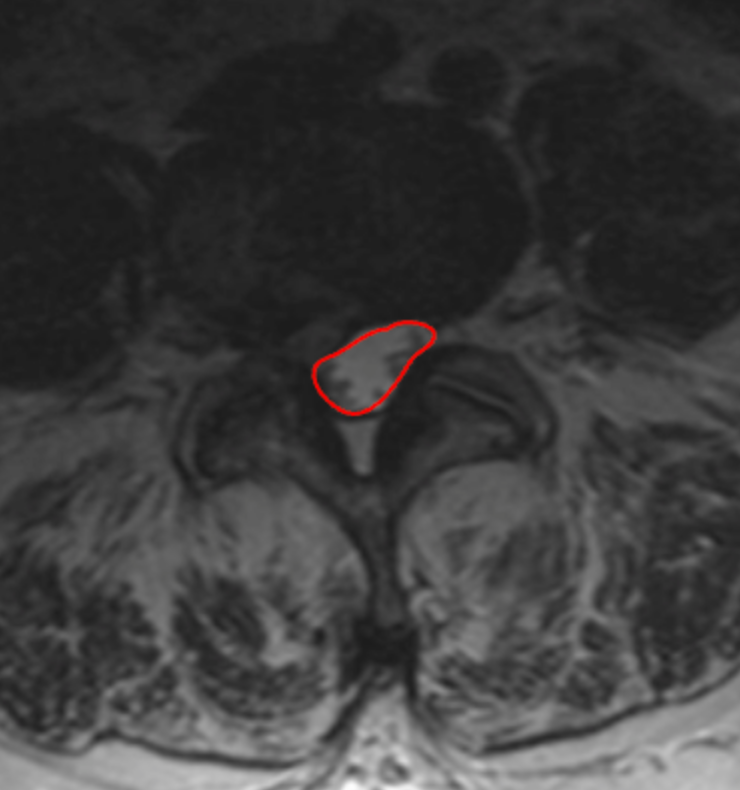
1) Description of Measurement
Dural sac CSA quantifies the cross-sectional area of the thecal sac within the lumbar spinal canal and directly reflects neural element compression from disc bulge, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, facet overgrowth, or spondylolisthesis.
This metric isolates the functional neural space, making it more clinically relevant than osseous canal area when evaluating lumbar spinal stenosis and neurogenic claudication.
2) Instructions to Measure
Use the sagittal T2 MRI to identify the lumbar level of maximal compression.
Scroll to the corresponding axial T2 slice at the disc or mid-vertebral level.
With a freehand ROI tool, trace the outer margin of the dural sac (CSF boundary), excluding epidural fat and ligamentum flavum.
Close the ROI to calculate the dural sac area in mm².
Record the smallest CSA across all lumbar levels.
3) Normal vs. Pathologic Ranges
Normal: > 100 mm2
Relative stenosis: 75 - 100 mm2
Severe stenosis: 50 - 75 mm2
Critical stenosis: < 50 mm2
Key points:
CSA < 75 mm² is strongly associated with symptomatic neurogenic claudication.
CSA < 50 mm² correlates with severe functional limitation.
4) Important References
Abel F, Tan ET, Chazen JL, et al. MRI after Lumbar Spine Decompression and Fusion Surgery: Technical Considerations, Expected Findings, and Complications. Radiology. 2023 Jul;308(1):e222732. doi: 10.1148/radiol.222732.
Hansen BB, Nordberg CL, Hansen P, et al. Weight-bearing MRI of the Lumbar Spine: Spinal Stenosis and Spondylolisthesis. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2019 Dec;23(6):621-633. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697937.
Genevay S, Atlas SJ. Lumbar spinal stenosis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010 Apr;24(2):253-65. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2009.11.001.
5) Other info....
Dural sac CSA is preferred over bony canal CSA because it reflects true neural compression.
Should be reported with:
AP canal diameter
Lateral recess depth
Foraminal area
Dynamic stenosis may be underestimated on supine MRI; consider axial-loaded or upright MRI when symptoms and CSA do not correlate.
Adapted from: Feger J, Er A, Yap J, et al. Lumbar spine protocol (MRI). Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 01 Jan 2026) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-147093